Banking has come a long way from the days of brick-and-mortar branches and paper-based transactions. Today, the financial world is shaped by two distinct approaches: classical banking and fintech banking. The ongoing evolution of the banking industry raises an intriguing debate: bank vs fintech. If you’re navigating this landscape and need expert advice, 1Office can provide the guidance you need to make the right choice. As traditional banks continue to innovate and fintech disrupts the financial ecosystem, understanding their differences has never been more important.
In today’s fast-paced business world, choosing the right banking solution is crucial. But with the rise of fintech, how do you decide between traditional banks and digital alternatives? This blog will delve into the key differences between these two solutions and their respective advantages and disadvantages, helping you choose the one that aligns with your needs.
Classical Banking
Classical banking, also known as traditional banking, is the established form of banking that has been around for centuries. It is characterized by physical branches, paper-based transactions, and a centralized system of governance. When considering bank vs fintech, classical banking remains the more traditional option, offering services like deposits, loans, and mortgages, and credit cards. When comparing classical banking vs fintech banking, the choice often depends on your preference for traditional stability or digital flexibility.
Classical banking provides a sense of security and a wide range of services. It is characterized by physical locations, personalized customer service, and a long-standing history of financial stability. These institutions are heavily regulated, ensuring customer protection and financial stability.
Regulations in Classical Banking:
Classical banks operate under strict regulatory frameworks designed to maintain the integrity of the financial system and protect consumers. These regulations typically include:
- Licensing and Supervision: Banks must obtain licenses from regulatory authorities and are subject to ongoing supervision to ensure compliance with financial standards.
- Capital Requirements: Banks are required to maintain a certain level of capital reserves to absorb potential losses and ensure solvency.
- Deposit Insurance: Many countries offer deposit insurance schemes, which protect customer deposits up to a certain limit in case of bank failure.
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) Regulations: Banks must implement robust AML and KYC procedures to prevent financial crimes and verify customer identities.
- Data Protection and Privacy: Banks are subject to strict regulations regarding the handling and protection of customer data.
Below you will find examples of classical banks in Estonia:
LHV Pank is a modern and customer-centric bank that has gained popularity in Estonia for its innovative digital banking solutions. It offers a range of financial products and services, such as current accounts, payment solutions, investment accounts, brokerage services, and business banking solutions. LHV Pank is known for its user-friendly online and mobile banking platforms, as well as its emphasis on technology-driven banking experiences.
Swedbank is one of the largest banks in Estonia, offering a wide range of financial services to individuals, businesses, and institutions. It provides savings and current accounts, loans, mortgages, investment products, and various banking solutions tailored to customer needs. Swedbank is known for its robust online banking platform and comprehensive suite of financial solutions, tailored to diverse customer needs.
SEB Pank is another prominent bank operating in Estonia, with a comprehensive suite of banking services for personal and business customers. It offers various banking products, including savings accounts, current accounts, loans, credit cards, investment services, and wealth management solutions. Recognized for its innovative approach to banking and focus on sustainable finance initiatives.
Coop Pank is a cooperative bank that focuses on serving the needs of its members and the local community. It provides a variety of banking services, including savings accounts, current accounts, loans, mortgages, and payment solutions. Coop Pank is committed to offering personalised service and supporting sustainable development initiatives, reflecting its cooperative values.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Classical Banking vs Fintech Banking.
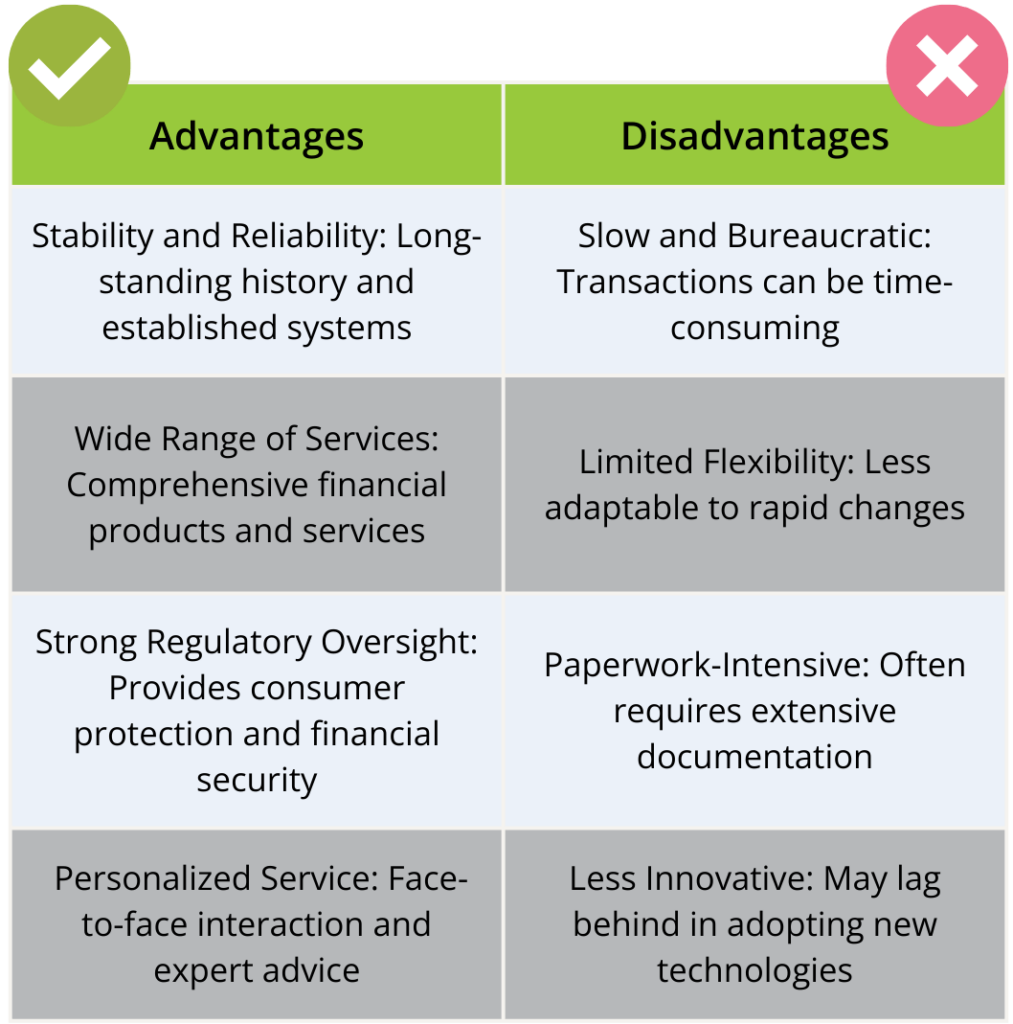
Advantages and Disadvantages of Classical Banking
When comparing bank vs fintech, the debate often revolves around stability versus innovation. The primary advantage of classical banking is that it is a tried and tested system that has been around for a long time. This makes it more stable and reliable than newer fintech banking solutions. Classical banking also provides a personal touch, as customers can interact with bank staff face-to-face and receive advice on their financial needs. The main disadvantage of classical banking is that it can be slow and bureaucratic. Transactions can take a long time to process, and there is often a lot of paperwork involved. Classical banking also tends to be less flexible and innovative than fintech banking solutions, as it is more focused on maintaining the status quo than disrupting it. So, remember: Choosing between a bank and fintech comes down to your specific financial needs.
Fintech Banking
Fintech banking, or digital banking, represents the cutting edge in the bank vs fintech comparison, that relies on technology to provide services. Fintech banking solutions are typically offered by online-only banks or by traditional banks that have adopted digital technology to streamline their operations. The role of regulation is crucial in maintaining the stability of classical banking vs fintech, where the latter often operates with fewer restrictions. The core services of fintech banking include online banking, mobile banking, and digital wallets.
Fintech banking prioritizes speed, convenience, and accessibility. By leveraging technology, fintech platforms offer innovative financial solutions that cater to the needs of the modern, digital-savvy consumer. Fintech banks generally have a lighter regulatory footprint than classical banks, but they are still subject to various regulations.
Fintech companies are subject to a growing body of regulations, which vary depending on the services they offer and the jurisdictions in which they operate. Common regulatory areas include:
- E-money Regulations: Many fintech platforms offering digital wallets or payment services must comply with e-money regulations, which govern the issuance and redemption of electronic money.
- Payment Services Directives (PSDs): In the European Union, PSD2 and PSD3 (upcoming) regulate payment services, including online payments and account information services.
- Data Protection (GDPR): Fintech companies handling customer data must comply with data protection regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the EU.
Here are some examples of possible Fintech solutions:
Revolut Business is a fintech platform that offers business accounts with a focus on flexibility and cost-effectiveness. Businesses can open multi-currency accounts, issue corporate cards, and access a suite of financial management tools through the Revolut Business platform. With features like instant payments, expense tracking, and budgeting controls, Revolut Business caters to the needs of modern businesses operating in a digital economy.
Revolut offers:
– Account with IBAN of the European Union (Lithuania), accounts can be opened online with no opening or maintenance costs, company cards (both physical and virtual).
-Multicurrency account: More useful for companies that operate internationally, it allows companies to make and receive payments in more than 25 currencies (EUR, GBP, USD etc).
-Corporate Cards: You can create 3 physical cards (the first one with free shipping costs) and up to 200 virtual cards per employee. This way you can manage the company’s daily expenses, and if any member of the team has to travel, you can also track them in real time.
-Revolut Pay: Focused on e-commerce shops, it is a payment gateway that integrates with the main E-commerce platforms (Woocommerce, Shopify, Presta Shop), it allows you to accept credit card payments. On the other hand they also have the option of payment links to issue invoices and customers to pay by card.
Wise is a global fintech company that offers borderless business accounts for companies engaged in international trade. With Wise Business, businesses can hold and manage multiple currencies, make international payments at low exchange rates, and access real-time financial insights. Wise’s transparent pricing and efficient cross-border payment solutions make it a preferred choice for businesses with global operations.
Paysera Business is a fintech company that provides business account services along with a range of financial solutions tailored to businesses of all sizes. Its business accounts offer features such as multi-currency support, payment processing, invoicing, and financial management tools. Paysera Business is known for its flexibility, competitive pricing, and commitment to security.
Airwallex is a global fintech company that offers business accounts and payment solutions designed for international businesses. With Airwallex Borderless Accounts, businesses can hold and manage multiple currencies, make cross-border payments at competitive exchange rates, and access advanced financial tools for managing global finances. Airwallex’s platform integrates seamlessly with e-commerce platforms and accounting software, making it ideal for businesses with international operations.
Wamo Bank is a fintech platform designed to simplify global business banking. It offers multi-currency business accounts, enabling companies to manage funds in 24 currencies with competitive exchange rates. Wamo provides features like local and international payments, invoicing, expense management, and virtual and physical Visa cards. Businesses can open an account online in just 10 minutes, making it an ideal solution for entrepreneurs and startups. With a focus on transparency, security, and user-friendly tools, Wamo empowers businesses to streamline their financial operations and scale globally.
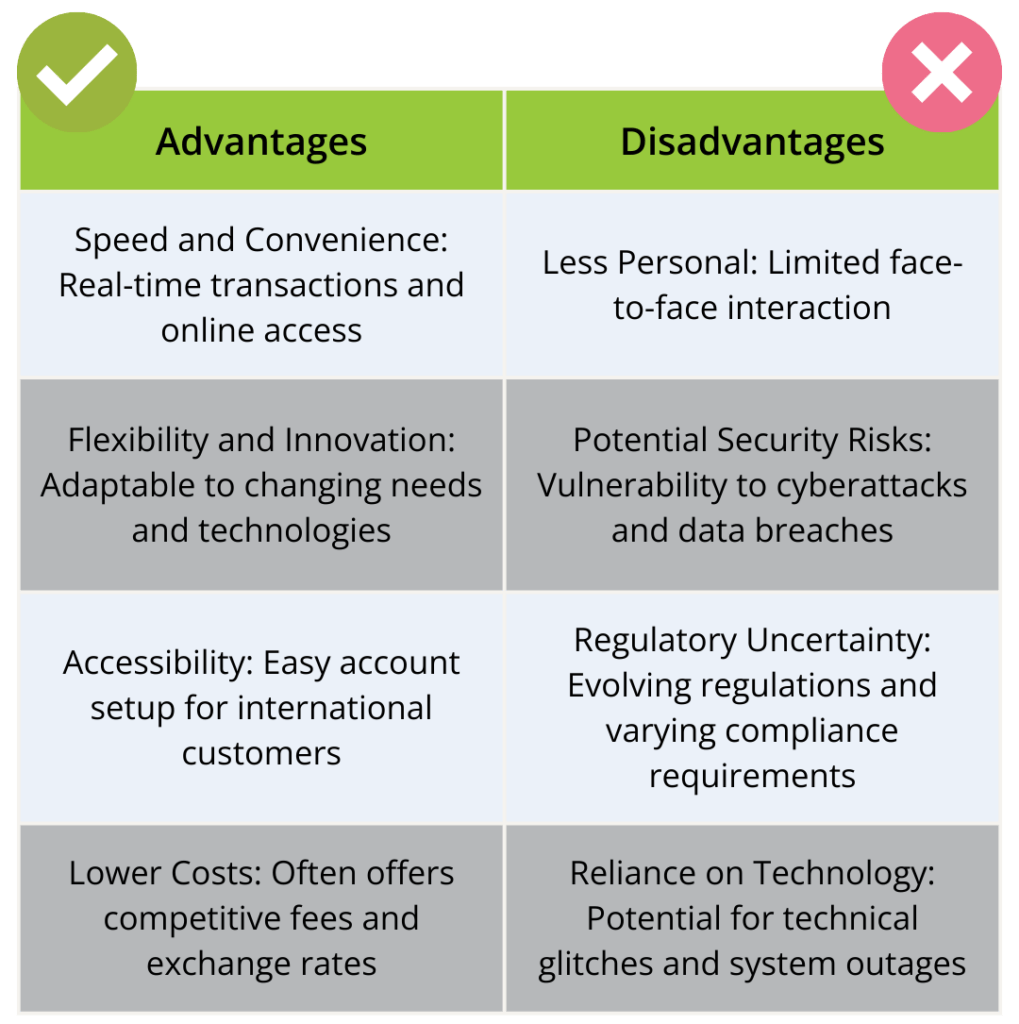
Advantages and Disadvantages of Fintech Banking vs Bank
The primary advantage of fintech banking is that it is fast, flexible, and convenient. Transactions can be completed in real-time, and there is no need to visit a physical branch – everything is done online. Fintech banking also tends to be more innovative than classical banking, as it is focused on finding new and better ways to serve customers. Fintech banks tend to be less personal than classical banks, as customers typically interact with digital interfaces rather than human staff.
However, a significant advantage in the bank vs fintech debate is the ease with which accounts can be opened online, even for international customers. Unlike classical banking, which may require in-person visits to a physical branch in Estonia, fintech platforms like Wise and Revolut allow you to set up an account from the comfort of your home with just a few clicks. As we explore the future of fintech and banking, these technology-driven platforms are likely to shape the global financial landscape further.
Use Cases:
- International Transactions: If you’re a small business owner who frequently makes international payments, a fintech platform like Wise might be a better fit, offering low exchange rates and fast transfers.
- Digital-First Businesses: For e-commerce businesses and digital nomads, fintech platforms like Revolut Business provide seamless online banking and multi-currency accounts.
- Quick and Easy Account Setup: If you need to open a business account quickly and remotely, fintech platforms offer streamlined online applications and instant verification.
Want tailored advice on leveraging these solutions? Turn to 1Office for expert consulting services – contact us.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the comparison between classical banking and fintech reveals a dynamic landscape in the financial sector, where traditional institutions and innovative technology-driven companies coexist and complement each other. Classical banks, with their long-standing reputation, stability, and extensive range of services, continue to serve as pillars of the financial system, providing essential banking services to individuals and businesses. On the other hand, fintech companies leverage technology to offer innovative solutions that enhance convenience, efficiency, and accessibility in banking, particularly for digital-native consumers and businesses with specific needs, such as international transactions and online payments. While classical banks emphasize trust, reliability, and personal relationships, fintech firms focus on agility, innovation, and user experience. In discussions about the future of fintech and banking, classical banking continues to innovate to stay competitive. The debate between classical banking vs fintech banking highlights the evolution of the financial industry. The coexistence of classical banking and fintech presents consumers and businesses with a diverse array of options, empowering them to choose financial services that best align with their preferences, needs, and priorities in today’s evolving digital economy.